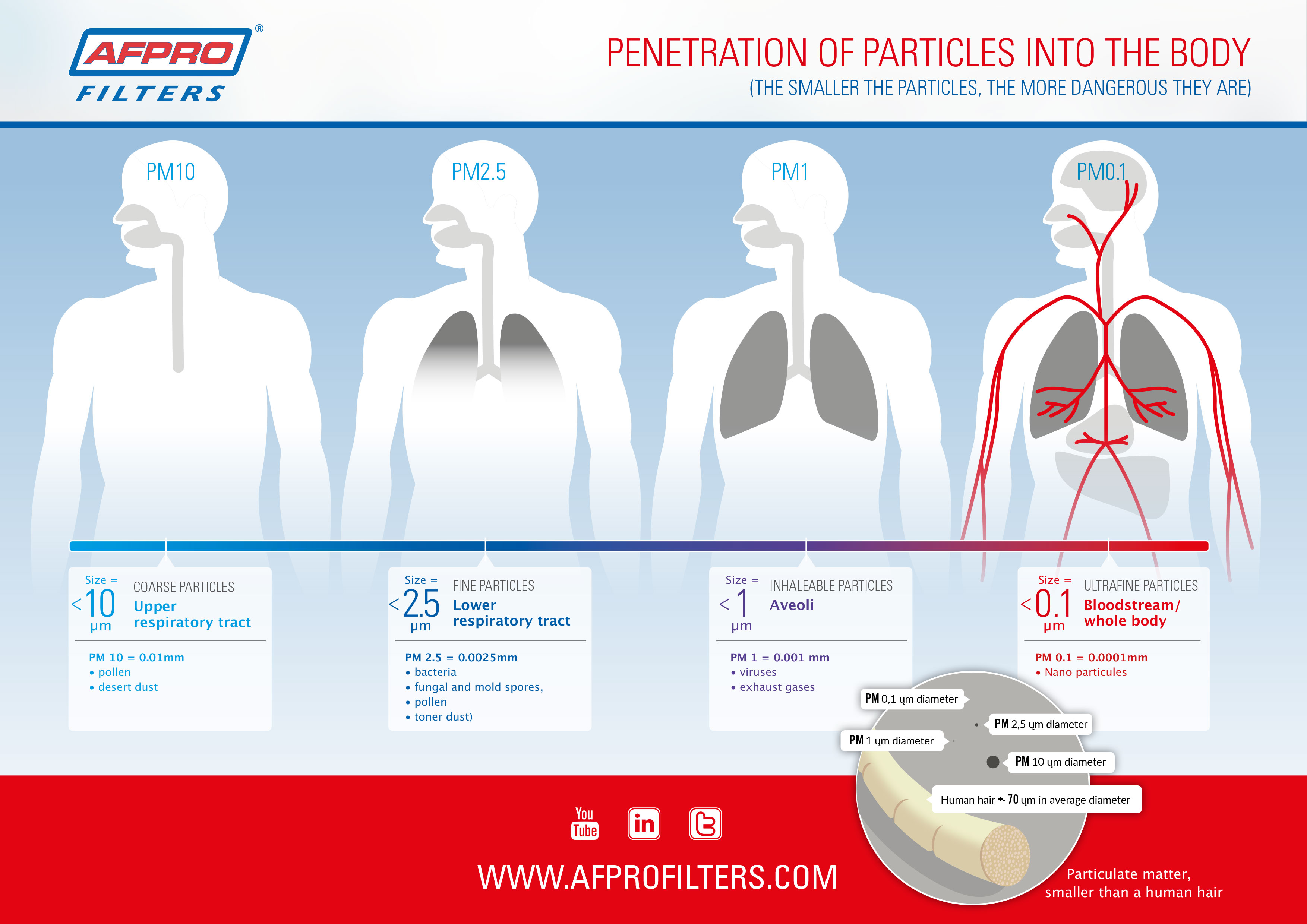
What is PM2.5, and why should you care? PM2.5, or fine particulate matter, is a major air pollutant that can have serious impacts on our health and the environment.
Particulate matter air filter - AFPRO - Source www.afprofilters.com
In this guide, we will explore the sources and health effects of PM2.5, as well as discuss what we can do to reduce our exposure to this harmful pollutant.
Key Differences: PM2.5 vs. Other Air Pollutants
| Characteristic | PM2.5 | Other Air Pollutants |
|---|---|---|
| Size | 2.5 micrometers or less in diameter | Varies, but generally larger than PM2.5 |
| Sources | Combustion engines, industrial processes, wildfires | Varies depending on the pollutant |
| Health Effects | Can cause respiratory and cardiovascular problems, as well as cancer | Can cause a variety of health problems, depending on the pollutant |
Sources of PM2.5
FAQ
This section provides answers to frequently asked questions regarding the impacts of PM2.5 on air quality and health, exploring misconceptions and shedding light on the importance of understanding this air pollutant's effects.
.png?width=1700&name=Particulate Matter Sizes (2).png)
A Guide to Understanding Particulate Matter (PM) - Source learn.kaiterra.com
Question 1: What is PM2.5?
PM2.5 refers to fine particulate matter, tiny particles with a diameter of 2.5 micrometers or less. These minute particles are often generated by combustion processes, including vehicle exhaust, industrial activities, and biomass burning.
Question 2: How does PM2.5 impact air quality?
PM2.5 contributes significantly to air pollution, reducing visibility and creating a hazy appearance. It impairs air quality by forming smog and exacerbating respiratory conditions.
Question 3: What are the health effects of PM2.5?
PM2.5 poses severe health risks, particularly for vulnerable populations. It can penetrate deep into the lungs and bloodstream, leading to respiratory illnesses, cardiovascular problems, and even premature death.
Question 4: How can I reduce my exposure to PM2.5?
To minimize PM2.5 exposure, consider using air purifiers indoors, wearing masks when air quality is poor, and avoiding outdoor activities during peak pollution hours.
Question 5: What are the sources of PM2.5 emissions?
Major sources of PM2.5 emissions include motor vehicles, power plants, industrial processes, and construction activities. Understanding these sources helps us develop targeted mitigation strategies.
Question 6: How can we improve air quality and reduce PM2.5 levels?
Improving air quality and reducing PM2.5 requires collaborative efforts. Governments can implement stricter emission regulations, promote cleaner energy sources, and support research on air pollution. Individuals can adopt sustainable practices such as using public transport or carpooling.
In conclusion, PM2.5 is a significant air pollutant with severe consequences for human health and the environment. Understanding its sources, effects, and mitigation measures is crucial for creating cleaner air and safeguarding public well-being.
Tips
This document provides crucial information on the serious impacts of PM2.5 on air quality and public health. Consider these tips to safeguard your well-being and minimize the adverse effects of fine particulate matter:
Tip 1: Monitor Air Quality
Stay informed about PM2.5 levels in your area. Check air quality forecasts and alerts through government agencies or reputable websites. This knowledge allows you to plan outdoor activities and take precautions when pollution levels are high.
Tip 2: Reduce Outdoor Activities When Necessary
On days with elevated PM2.5 levels, limit prolonged or strenuous outdoor activities, especially for at-risk individuals such as children, the elderly, and those with respiratory conditions. Consider alternative indoor activities or adjust outdoor plans to times when air quality is better.
Tip 3: Use Air Purifiers
Equip your home, office, or school with high-quality air purifiers that can effectively remove PM2.5 particles from the air. These devices can significantly improve indoor air quality and reduce exposure to harmful pollutants.
Tip 4: Invest in Particulate-Filtering Masks
When unavoidable outdoor exposure is necessary, protect yourself with particulate-filtering face masks, such as N95 or KN95 respirators. These masks effectively block out a significant portion of PM2.5 particles, reducing the amount of pollution inhaled.
Tip 5: Promote Public Awareness
Spread awareness about the health risks associated with PM2.5 and the importance of reducing exposure. Share information with friends, family, and colleagues. Encourage collective action to address air pollution sources and advocate for improved air quality standards.
By adopting these practical tips, you can take proactive steps to mitigate the adverse effects of PM2.5 on your health and well-being. Remember, every effort counts in the fight against air pollution and the protection of our collective respiratory health.
To explore further details and scientific evidence on the impacts of PM2.5: Understanding The Impacts Of Fine Particulate Matter On Air Quality And Health, refer to the comprehensive article. Together, we can create a cleaner, healthier environment for present and future generations.
PM2.5: Understanding The Impacts Of Fine Particulate Matter On Air Quality And Health
PM2.5, fine particulate matter with a diameter of less than 2.5 micrometers, poses significant threats to air quality and human health. Its adverse effects extend to various aspects, including:
- Respiratory Health
- Cardiovascular Risks
- Visibility Impairment
- Ecosystem Damage
- Economic Costs
- Global Climate Change
These key aspects reveal the multifaceted nature of PM2.5's impacts. Respiratory health is compromised due to PM2.5's ability to penetrate deep into the lungs, leading to asthma, bronchitis, and other ailments. Cardiovascular risks increase as PM2.5 can damage blood vessels and contribute to heart disease. Moreover, PM2.5 reduces visibility by scattering sunlight, affecting transportation and aesthetics. It also harms ecosystems by damaging plants and water bodies. The economic burden is significant, with costs associated with healthcare, lost productivity, and reduced tourism. Lastly, PM2.5 contributes to climate change by affecting cloud formation and altering Earth's energy balance.

Figure 2 from Fine particulate matter (PM2.5): The culprit for chronic - Source www.semanticscholar.org
PM2.5: Understanding The Impacts Of Fine Particulate Matter On Air Quality And Health
PM2.5 is fine particulate matter that measures 2.5 micrometers or less in diameter. These tiny particles are a major component of air pollution and can have significant impacts on both air quality and health.

Particulate Matter: The Overview | Earth.Org - Past | Present | Future - Source earth.org
PM2.5 particles can come from a variety of sources, including vehicle exhaust, industrial emissions, and wildfires. When inhaled, PM2.5 particles can lodge deep in the lungs, where they can cause a variety of health problems, including:
- Respiratory problems, such as asthma and bronchitis
- Cardiovascular problems, such as heart disease and stroke
- Cancer
PM2.5 pollution is a major problem in many parts of the world, and it is estimated to cause millions of premature deaths each year. In the United States, PM2.5 pollution is responsible for an estimated 100,000 premature deaths each year.
There are a number of things that can be done to reduce PM2.5 pollution, including:
- Reducing emissions from vehicles and industrial sources
- Promoting the use of clean energy sources
- Improving energy efficiency
- Planting trees and other vegetation
- Educating the public about the health risks of PM2.5 pollution.
By taking these steps, we can help to reduce PM2.5 pollution and improve the quality of the air we breathe.